When buying in international trade, it’s crucial to know which trade terms can benefit you the most. Understanding the differences between the terms of trade will make you reduce your import prices. And it will also make your E-Commerce buying experience more accessible.
We’ve experienced using each of the trade terms in different international sales contracts during our ten years of experience. May it be EWX, CIF, FCA, or you name it, we know exactly how it’s done.
If you want an overview of what trade terms are, continue reading!
What are Trade Terms?
Trade terms are the terms of a transaction between a supplier and a buyer. You can use it in both domestic and international trade. But, it’s usually used more often in the latter. In this trade agreement, buyers and sellers negotiate and decide who shoulders specific risks, costs, and responsibilities associated with the goods shipped.
The responsibilities and costs mentioned in terms of trade are:
- Loading costs
- Carrier expenses
- Freight costs
- Transportation costs
- Insurance expenses
- Import and export license
- Unloading expenses
- Custom duties
Each term of the trade sales contract divides these responsibilities between the two parties differently. In some terms of trade, the seller bears most of these responsibilities. While in some trade terms, the buyer is responsible for most expenses and documentation of their imported goods.
It’s important to know which trade terms are suitable for your given market. This way, you’ll have a perfect balance between reducing expenses and having comfort while buying from suppliers.
What are the different roles in Trade Terms?
- Sellers: Sellers can be manufacturers, suppliers, or wholesalers. It’s important to know what responsibilities the export prices of sellers include. It’s easy to spend more money in foreign markets unintentionally.
- Buyers: Buyers are the individuals or businesses purchasing the services produced by the seller. Buyer bears different responsibilities depending on the terms of a trade agreement. In those terms, consider yourself or me as a buyer.
- Freight forwarders: Freight forwarders are firms that make shipping arrangements from a particular country to a named overseas post.
- Carrier: The entity responsible for transporting the goods. They usually transport cargo from the seller’s warehouse to the shipping port.
- Destination point: This is where the responsibilities and risks transfer from the seller to the buyer. Most of the time, both delivery points are the same, but in some trade terms, they differ.
- Destination port: This is usually the port in the buyer’s country for international trade. As I trade in the US so my destination ports are mostly US ports.
What are the commonly used trade terms?
A:
Ad Valorem Tariff:
It means that the customs duty is measured by considering a percentage of the value of the products or services, i.e., 10 % Ad Valorem means 10 % of the total amount of subjected goods.
ATA Carnet:
The ATA Carnet is an illustration of how close collaboration between customs and business can facilitate international trade. Every country in ATA Carnet has a guaranteeing body that is approved by the WCF and national customs authorities.
The guaranteeing organization can issue Carnets and can also authorize local chambers to deliver carnets on its behalf. ATA enables the temporary importation of goods into overseas countries by removing tariffs and value-added taxes
B:
Bill of Lading:
It is a document issued by the transporter or carrier to acknowledge the receipt of goods for shipment. For vessels, two types of it for Vessels exist shipper’s order (negotiable) and straight bill of lading (not negotiable). It is the most important document while shipping so I keep it carefully.
Bonded Goods:
These are dutiable landed imports, stored in a bonded warehouse under the customs authorities. These products are subject to be released upon the payment of taxes, import duties payment, and other charges.
Brokerage:
A person or company that acts as a middleman between seller and buyer to clear inbound or outbound shipments. My brokerage partner helps me to sort out things with the supplier.

C:
Carnet:
A Carnet or ATA Carnet is a temporary import-export document in international customs. It is used for the clearance of customs in almost eighty-seven countries without paying taxes and duties on goods that are exported within 12 months. Therefore, carnets are also called as a passport or merchandise passports of Goods.
According to the ATA Convention, professional and commercial travelers can bring commercial samples, advertising materials, or other professional equipment with them into member countries without paying taxes and duties.
Certificate of Origin:
This document certifies that the products relate to originated from which particular country, hence called a certificate of origin. It can also include a declaration by producer, manufacturer, exporter, supplier, or another qualified person.
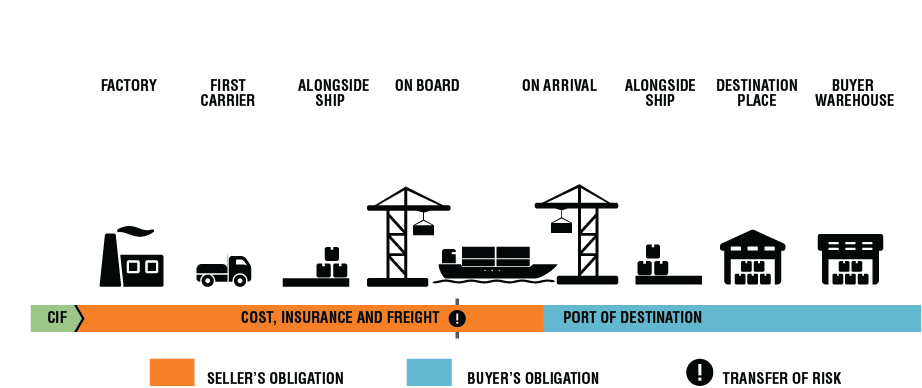
CIF stands for Cost, Insurance, and Freight. This means that the product seller delivers his part of the contract when products pass the ship’s rail on a port.
The seller is supposed to pay the essential freight and costs to bring the products to the decided port.
The risk of damage or loss to the product, including additional costs, if occurred due to certain events after the delivery time, will be transferred to the buyer. In those cases, I try to buy good insurance to manage the losses.
Commercial Invoice:
Commercial Invoice is a legal document that exists between the supplier and the buyer in which the product details and its amount is specified. Therefore, it is one of the essential documents required for the determination of customs duties.
Commodity:
A commodity is a fundamental product being used in commerce. It is interchangeable with other similar products. Generally, the commodity is referred to as the raw materials that are used to produce other products.
These also include minerals such as copper, manganese, and tin; and agricultural products such as tea, rubber, and coffee.
Consumer Goods:
Consumer goods are goods used for consumption by the end consumer. Also called as final goods, these are the result of manufacturing and production. Consumers will view these stocked on the store shelf, i.e., food, clothing, and domestic products.
Consumption:
Consumption is purchasing and utilization of products or services for human desire satisfaction. Consumption also means utilizing goods and services to produce other goods or services. Hence, the consumer may be a human being, a business entity, or a public body.
Cost and Freight (CFR):
Cost and freight refer to legal terms that are used in contracts in international trade. It explains that the seller of products is considered to arrange the carriage of goods to a port of destination.
Further, it also includes providing the buyer with the necessary documents needed to carry on terms from the carrier.
Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF):
CIF is an expense that is paid by the seller to cover the costs, insurance, and freight buyer’s order when goods are in transit. I try to convince my sellers on this term because it lowers my part in shipment.
The goods are shipped to a port decided in the sales contract. Seller takes the responsibility for these costs until these goods are fully loaded onto a transport ship.
Countervail able Subsidy:
It is financial assistance from foreign governments to benefit the production of products from overseas companies. It is limited to a particular industry or enterprise. These subsidies depend upon either export performance or the use of domestic products over imported goods.
Countervailing Duties (CVD):
Countervailing duties are anti-subsidy and trade import duties that are imposed under the World Trade Organization (WTO). These are to neutralize the harmful effects of subsidies. When a country subsidies its export on the cost of domestic products, these costs are imposed.
Customs Declaration:
These documents are used and accepted by the Customs. It is an action or statement, approved or prescribed by the Customs to render information or particulars.
D:
Demand:
Demand is an economic term that refers to a buyer’s desire to buy products and services and willing to pay the price of those products and services. Therefore, demand is strongly influenced by a buyer’s preference in a market economy.
De Minimis:
De Minimis is a Latin term drawn from the expression “de minimis non curat lex.” It means that law is not to consider the small matters. This term is deemed to be valid when waiving off tiny amounts of taxes and duties.
Dumping:
Dumping is a terminology being used in international trade. When a company or country exports products at a price that is less in foreign markets than exporter’s countries market, it is called Dumping.
E:
E-Commerce:
E-Commerce is the short form of Electronic commerce in which buying and selling of products and services are done through an electronic network. I have many eCommerce stores and I sell products through online stores.
Mostly, it is the internet. Business transactions happen in any form as B2B (business to business), B2C (Business to Consumer), or C2C (Consumer to consumer).
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN):
An Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) is utilized in the Commerce Control List to determine whether an export license is required by the subject products or not? It is a five-character alpha-numeric code.
Electronic Export Information (EEI), formerly known as Shipper’s Export Declaration:
Electronic Export Information (EEI) is an electronic data maintained in an Automated Export System (AES). It is used to control the mechanism of export by source documents. EEI is needed for shipments whose commodities’ value exceeds $2,500.
Embargo:
The embargo is taken from the Spanish language. It means obstruction, hindrance, etc. In a business sense, it refers to a trading ban. It is the complete or partial prohibition of trade and commerce with a particular state, country, or territory. My international clients often experience these bans due to instabilities between Govts.
Exports:
Exports are the goods and services that are produced in a particular country and sold in another country. These are sold for any settlement of debt, foreign exchange, gold, money, or goods and services.
Countries dedicate their domestic resources to produce these goods and services to export for the betterment of their economy in international markets.
F:
Free Trade Agreements:
Free Trade Agreements (FTA) is a treaty that refers to a multinational agreement following international law. This agreement allowed the countries to enter a free-trade area. FTAs are pursued to eliminate trade barriers by determining tariffs and duties between countries.
G:
Goods:
In business, goods are referred to as the items that satisfy human needs and wants and provide utility.
Goods and Services Tax (GST):
It is a value-added tax imposed on goods and services mostly sold for domestic consumption. Eventually, it affects both importer and the exporter. As my outsourcing is very diverse it means I have to pay it many times.
H:
Harmonization:
The process of making procedures or measures applied by different countries — especially those affecting international trade—more compatible, as by effecting simultaneous tariff cuts implemented by various countries to make their tariff structures more uniform.
Harmonized System:
This system is published by the World Customs Organization. It is a system of numbers and names to classify traded products. Goods are organized into chapters, sub-chapters, and sections that are governed by rules.
I:
Imports:
This term refers to the goods and services that are brought to a country from another country. When a country finds its resources insufficient to produce particular products, they have to import. Countries mainly do it to enhance their people’s welfare. As I outsource from other countries, it is imported from those countries.
Companies also import goods for their business terms. For example, a manufacturer imports raw material from other countries to produce products and services.
Importer of Record (IOR):
Importer of Record (IOR) is a customs law term. It is referred to as an importer who is held responsible for ensuring that he/she is dealing with legal goods. Further, these legal goods must be following both countries’ (supplier’s country and importer’s country) law.
The importer can be a person or business entity and is responsible for filing required legal documents. Authorities assess the products and services through these documents.
Incoterms:
Incoterms is the short form of International commercial Terms. These are rules that explain the responsibilities of buyers specifying a sales contract in both domestic and international trade. These instructions are published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
Incoterms are widely acceptable in international commercial transactions. The recent update had organized the modes of transport. These are effective since January 2010. Some of the frequently used Incoterms are as under;
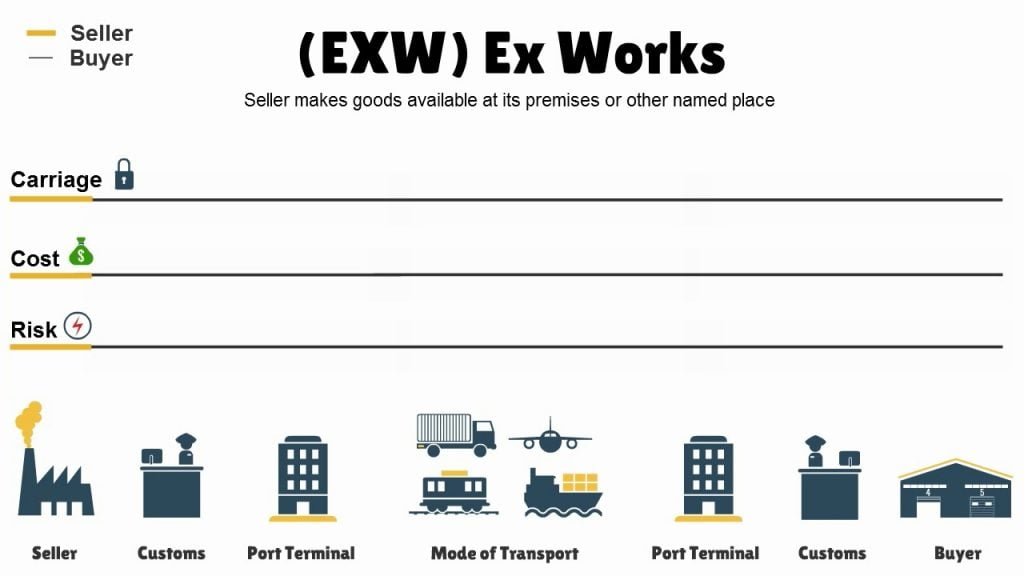
- Ex Works (EXW): It means that the seller is responsible for the accessibility and availability of the products at his/her factory or warehouse only. The buyer is responsible for picking goods from there.
- Free Carrier (FCA): In this Incoterm, the seller takes the responsibility of customs clearance from the country of origin. Further, the seller is responsible for delivering goods to a decided destination also.
- Carriage Paid To (CPT): Seller takes the responsibility to arrange customs clearance, pay export fees, and organize and pay the carrier to deliver goods at a pre-arranged place.
- Carriage and Insurance Paid to (CIP): It is similar to Carriage Paid to, with some exception. The seller is responsible for the insurance of the goods while these are in transit.
- Delivered at Terminal (DAT): In this incoterm, the seller provides the products to the buyer at the agreed port or terminal. The seller bears all associated costs and risks but has no responsibility to unload the products.
- Delivered at Place (DAP): The seller provides products to the buyer at the time when the truck arrives at the agreed place. The buyer is responsible for unloading, and the risk is transferred from seller to buyer.
- Delivered Duty Paid (DDP): In this incoterm, the seller takes the responsibility of the complete transport process. The responsibility and risks are transferred to the buyer only when he/she receives the products. It is usually a good deal for me as I only get responsible when I receive it.
Suggested reading: Alibaba DDP Shipping
L:
Landed Cost:
It is the total cost incurred on goods on its journey from manufacturers to buyer’s doorstep. It mainly includes goods price, insurance fees, shipment fees, customs duties, and any other changes. I add landed cost with further transportation to check my total shipping charges.
Letter of Credit:
It also is known as a credit letter is a guarantee from the bank that the buyer will pay the seller the decided amount of money on the decided time.
The buyer buys goods or products from the seller on credit. Bank mediates and facilitates this transaction with security. If the buyer defaults, the bank will pay the amount.
M:
Market Access:
Market access is referred to as the ability to penetrate in domestic trade. It is also referred to as the ability of a country or firm to sell products beyond the borders. However, the former is considered the most common in context.
Market Economy:
A market economy is an economic setup in which price signals created by the market forces decide regarding production and distributions. Mainly market forces here mean the supply and demand function of a particular product.
Market Forces:
Market Forces are the forces that directly or indirectly affect the demand and supply function of products in a market. Generally, these are associated with buyers and sellers to cause the deviations in prices without being controlled by governments.
O:
Origin:
An origin is a place where a product or service is produced. At origin, the goods are manufactured and then prepared for the shipment. In international trade, the country exporting products is called the country of origin. My sourcing is from Chinese manufacturers so the good’s origin is China.
P:
Phytosanitary Certificate:
Phytosanitary certification is used to verify that a shipment meets the phytosanitary import requirements. It is issued by a National Plant Protection Organization. It is usually applicable to import agriculture products.
The certificate certifies that the products that are being exported or imported are free from dangerous pests and plant diseases.
Pro-forma Invoice:
A Pro forma invoice is an initial bill of sale that is sent to the buyer in advance to a consignment or shipment of products. Generally, this invoice describes the purchased items with quantity, rates, transport charges, and shipping weight, etc.
Prohibited Commodities:
These are commodities which hare prohibited in a country by law and regulation. Therefore, importer and exporter have to consider legal status in particular countries. In those cases, I have to go through a long legal process to import such sensitive chemicals. If you are a small business then don’t do it because it would waste your time.
R:
Restricted Commodities:
Some commodities are restricted in a particular country or region. Companies are bound to obey the rules and regulations. Therefore, they are required to take approval and maintain the necessary documentation for shipment.

S:
Schedule B:
Schedule B is the classification of the products for export in the form of a ten-digit number. This number is used by the Bureau of Census to Collect Trade Statistics in the United States of America.
Shipper:
A shipper is a person who is given the responsibility to transport goods and commodities. In the shipping industry, the role of a shipper is of critical importance and, therefore, cannot be overlooked.
Subsidy:
A subsidy is a type of financial support or aid given to an economic entity (individual or business). The purpose of this is to promote social and economic policies.
This aid is provided by a government in general. However, the term subsidy can be associated with any type of support, i.e., NOGs or implicit subsidies.
Supply:
Supply is referred to the quantity of an economic product; a seller can offer at a particular price at a specific time.
In a market economy, supply is typically determined by the response of many entrepreneurs and companies. Their perception of the cost and profit margin affects the scenario.
Surplus:
A surplus in the market happens when the supply of particular products exceeds demand. In this situation, some manufacturers of that product are not in a position to sell all their goods. Hence, they will be willing to lower the price to make sales.
T:
Tariff:
When buyers from a country import goods from sellers of another country, they have to pay some taxes. These taxes are called tariffs. Tariffs increase the cost of goods and eventually result in a high price of products. Therefore, organizations also take a look at these tariffs to minimize their cost. I also add a tariff in my sourcing price to see if is it viable to do or not.
Trade Agreement:
It is also known as a trade pact. It is a wide-ranging tariff, taxes, and trade treaty that generally includes investment guarantees. It occurs when two or more countries decide and agree on terms that facilitate their trade with each other.
Trade Barriers:
Trade barriers are governmental restrictions on international trade. Economist generally explains that trade barriers are not beneficial and decrease the overall economic efficiency.
However, in a good sense, these are also helpful in safeguarding domestic products from foreign substitutes.
Types Of Export:
Initially, I got easily confused between exports while starting my business. As time takes I get profound in differentiating between their types. There are typically three various types of exports.
- Permanent Export: In this export, products are exported permanently and are not intended to be imported back.
- Temporary Exports: In temporary export goods can be imported back to the country of origin.
- Repair/Return Exports: Products can be exported to other countries for repairing, testing, processing, or any other purpose, and these are re-imported then.
Suggested reading:Best China Export Agent Make It Easier To Import From China

Frequently Asked Questions
Trade Terms is a comprehensive set of rules. These are very helpful when two or more countries or companies from different countries come into a business transaction. To ease the readers, we have answered some of the most frequently asked questions.
· What are the most commonly used trade terms?
Commonly used trade terms are those who are accepted by most countries worldwide. Therefore, in this context, these are referred to the international commerce terms. Hence, the most commonly used trade terms are as follows
- EXW (EX-Works)
- FOB (Free On Board)
- FCA (Free Carrier)
- FAS (Free Alongside Shipment)
- CFR (Cost and Freight)
- CIF (Cost, Insurance and Freight)
- CPT (Carriage Paid To)
- CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To)
- DAF (Delivered At Frontier)
- DES (Delivered Ex Ship)
- DEQ (Delivered Ex Quay)
- DDP (Delivered Duty Paid)
- DDU (Delivered Duty Unpaid).
· What are International Trade Terms?
International Trade terms are the standard terms in a trade that explain the rights and responsibilities of the parties making transaction.
It elaborates on the obligations of the buyer and seller by explaining the deal and its cost aspects. These aspects include carriage, transportation, insurance, as well as insurance, etc.
When buyers and sellers relate to different countries, then the uses of these terms are encouraged by the trade councils, international lawyers, and courts. Both parties (seller and buyer) not only build confidence but also solve issues if they arise.
· What are the terms of trade effect?
A change in trade policy affects the price level/index of the composite good and relative prices of diverse varieties. Export Supply elasticity, substitution elasticity, and import demand elasticity always tend to neutralize the effects.
However, trade effects lead to changes in the selected aggregate level of spending on the product. It also affects the composition of the sourcing of that product. Eventually, both channels affect the bilateral trade flow.
· What are the limits of the terms of trade?
Trade terms always cannot solve each problem. These have some limits. In case of default seeking protection through ICC or the laws of your country can be tricky. Trade terms cannot be applied to every product if it relates to some particular class.
· What is the difference between FOB and CIF?
In CIF, the seller takes primary ownership until the delivery of products. Hence, the seller is responsible for insurance costs and risks until the products reach the decision point of destination with the buyer.
Whereas in FOB seller is responsible for the products up to the nearest port on his/her end. Therefore, new buyers are recommended not to use FOB because they are supposed to retain the responsibility of products while in shipment.
· Is international trade good or bad?
Whether international trade is good or bad depends upon the situation. For some people, it is good, and for some, it is terrible. Some advantages of international trade include;
- Countries can use their natural resources optimally in international trade.
- It facilitates a business to reach raw materials that are not available in domestic markets.
- In international trade, products can be manufactured not only for domestic but also for global markets.
- A business in international trade can bear price fluctuations better than a company in domestic markets only.
- It enables a business to produce more and more quality products at less price; hence they can Increase their efficiency
- It gives a chance to interact with the people of other countries that can bring value and innovate ideas into business.
Foreign trade is not without disadvantages. Some of the disadvantages are as follows;
- Developing countries have to rely on developed countries. In international trade, exporting country is always at a benefit.
- It is the need of underdeveloped countries to depend on the developed ones for their better economic development.
- International trade always has some impacts and pressure from the political parties.
- International trade also affects domestic industries.
· How do you calculate terms of trade
When countries import and export a massive amount of products and services, they use the following formula to calculate terms of trade;
TOT = [Index of export price (PX) / index of import price (Pm)] x 100
Suggested reading: Import Tax From China To US

How LeelineSourcing Help You Better understanding of Trade Terms:
LeelineSourcing is amongst the top sourcing agents in China. Having decade-plus experience in international trade, LeelinSourcing can help their customers in various ways.
If you want to do business transactions in China and are worried about trade terms, do not worry.
LeelineSourcing’s diversified services include product sourcing, quality inspection, FBA Prep Services, FBA forwarding Services under the trade terms defined by various countries.
Leelinsourcing will help you throughout the process from finding a suitable manufacturer to the delivery of products at your doorstep.
Suggested reading:How To Buy From China: Ultimate Guide
Final Thoughts on Trade Terms
Today is the era of globalization. It is central for every business to add an international perspective to remain competitive in the market.
Enterprises are striving to increase their strengths by the inclusion of diversity to tackle the threats in the market environment.
At the same time, it is challenging to transact in another country due to several reasons. Therefore, trade terms are settled between countries to catch these opportunities to boost up the economy. However, we also have to consider the limits of trade terms at the same time.